Exploring the Future of AI Agents

Introduction
AI agents are transforming the landscape of generative AI, enabling developers to create sophisticated applications that interact seamlessly with the external world. These agents leverage large language models (LLMs) to perform tasks ranging from simple tool usage to complex planning and memory retention. The following explores the insights shared by experts in the field about the current state and future of AI agents.
Understanding AI Agents
AI agents represent a significant advancement in the use of LLMs. Instead of merely responding to prompts, these agents engage in iterative processes, making decisions, executing actions, and learning from their outcomes. This approach can be likened to running an LLM in a loop: asking it what to do, executing the action, and repeating the process until a satisfactory result is achieved.
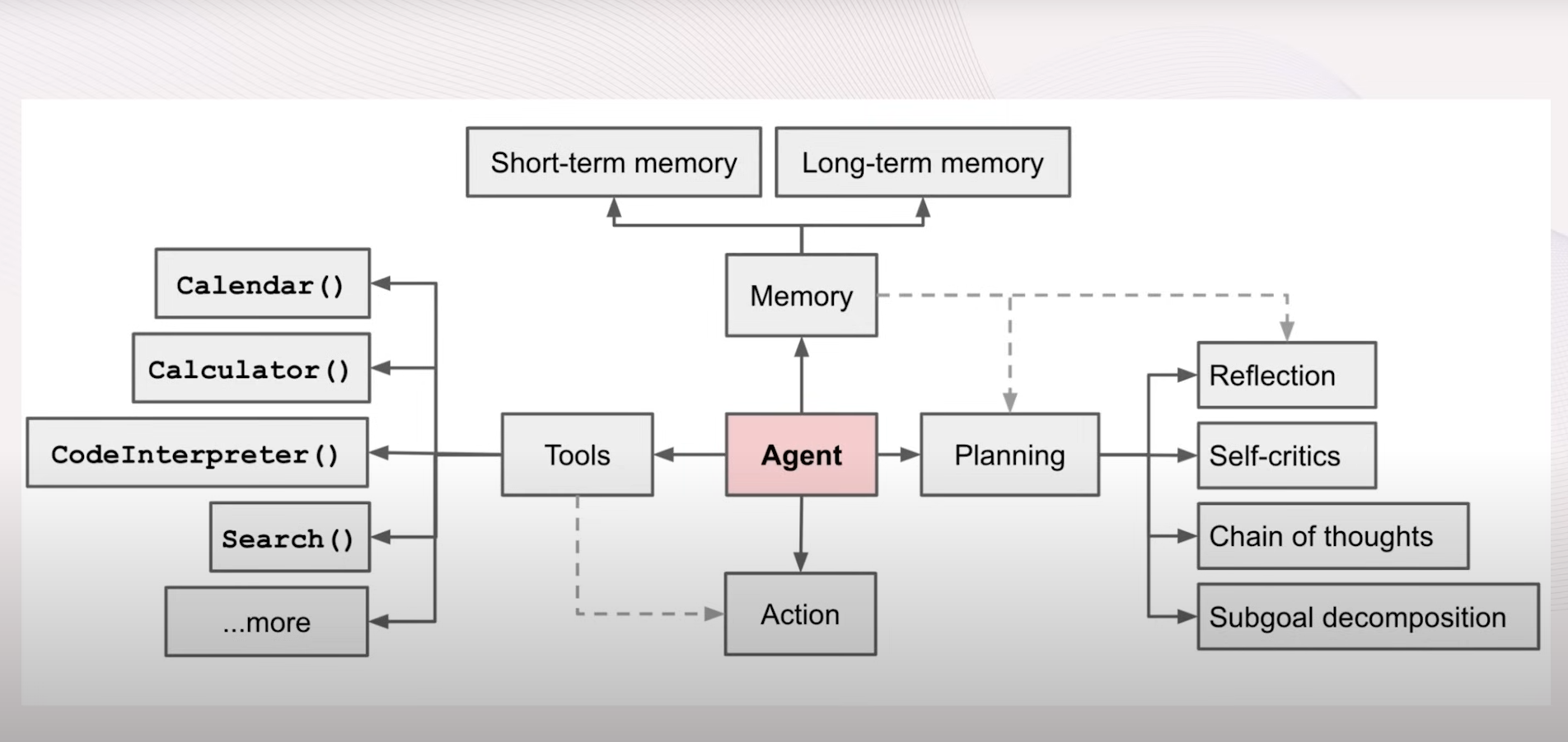
Key Areas of Focus
Planning
One of the core components of AI agents is planning. When running an LLM in a loop, multiple steps are often required. Current language models struggle with autonomous planning, necessitating external prompting strategies. These strategies, whether for initial planning steps or reflection at the end, ensure that the AI agent can reason about its actions and plan effectively. The future may see these strategies integrated into the models themselves, reducing the need for external prompts.
User Experience (UX)
The user experience of AI agents is crucial for their effectiveness. Human-in-the-loop remains essential due to the current limitations of AI reliability. However, finding the right balance is key. One promising UX feature is the ability to rewind and edit the agent's actions, allowing users to correct and guide the AI. This feature not only increases reliability but also enhances the user’s control over the AI’s actions, making the interaction more intuitive and effective.
Memory
Memory is another critical aspect of AI agents. Effective memory systems enable agents to learn and remember both procedural tasks and personalized user information. Procedural memory allows the AI to improve its performance over time by remembering how to perform tasks correctly. Personalized memory, on the other hand, tailors the AI’s responses based on individual user preferences and past interactions, creating a more personalized and engaging experience.
Practical Applications of AI Agents
The practical applications of AI agents are vast and varied. They can be used for everything from writing essays to coding complex software. By adopting an agentic workflow, AI systems can draft, revise, and iterate on their outputs, delivering superior results compared to traditional, non-agentic methods.
Design Patterns in AI Agents
Several design patterns have emerged as particularly effective in the development of AI agents:
Reflection
Reflection involves the AI reviewing its own work to ensure correctness and efficiency. By prompting the AI to reflect on and critique its own outputs, developers can significantly enhance the quality and reliability of the results. This method allows the AI to identify and rectify errors, leading to more accurate and efficient outcomes.
Multi-Agent Collaboration
Multi-agent systems involve multiple AI agents working together, each taking on specific roles such as coder, critic, or manager. This collaborative approach leverages the strengths of different agents to achieve complex tasks more effectively. Multi-agent collaboration has been shown to significantly boost the performance of AI systems, making them more versatile and capable.
Tool Use
AI agents can use various tools to expand their capabilities. For instance, they can perform web searches, generate and run code, and manipulate images. This tool use allows AI agents to handle a wider range of tasks and enhances their utility in real-world applications.
Planning
Planning algorithms enable AI agents to autonomously navigate around obstacles and failures. This capability is crucial for complex tasks that require flexibility and adaptability. By incorporating planning algorithms, AI agents can become more robust and reliable, capable of handling unexpected challenges with ease.
Conclusion
AI agents represent a transformative step forward in the field of artificial intelligence. By integrating planning, reflection, tool use, and multi-agent collaboration, developers can create more sophisticated, reliable, and capable AI systems. As these technologies continue to evolve, the potential applications and benefits will expand, driving innovation and improving our interactions with AI.
The future of AI agents is bright, and their continued development promises to unlock new possibilities and enhance our capabilities. Embracing these advancements will be key to staying at the forefront of AI innovation and leveraging its full potential.